Table Of Content

You may lose hair just on your head or from your body as well. There are several ways to prevent further hair loss and slow down the thinning process. Newer treatment options are being developed and becoming available. These new treatments might be able to help regrow hair. Most baldness is caused by genetics (male-pattern baldness and female-pattern baldness).
It's not too late to save thinning hair
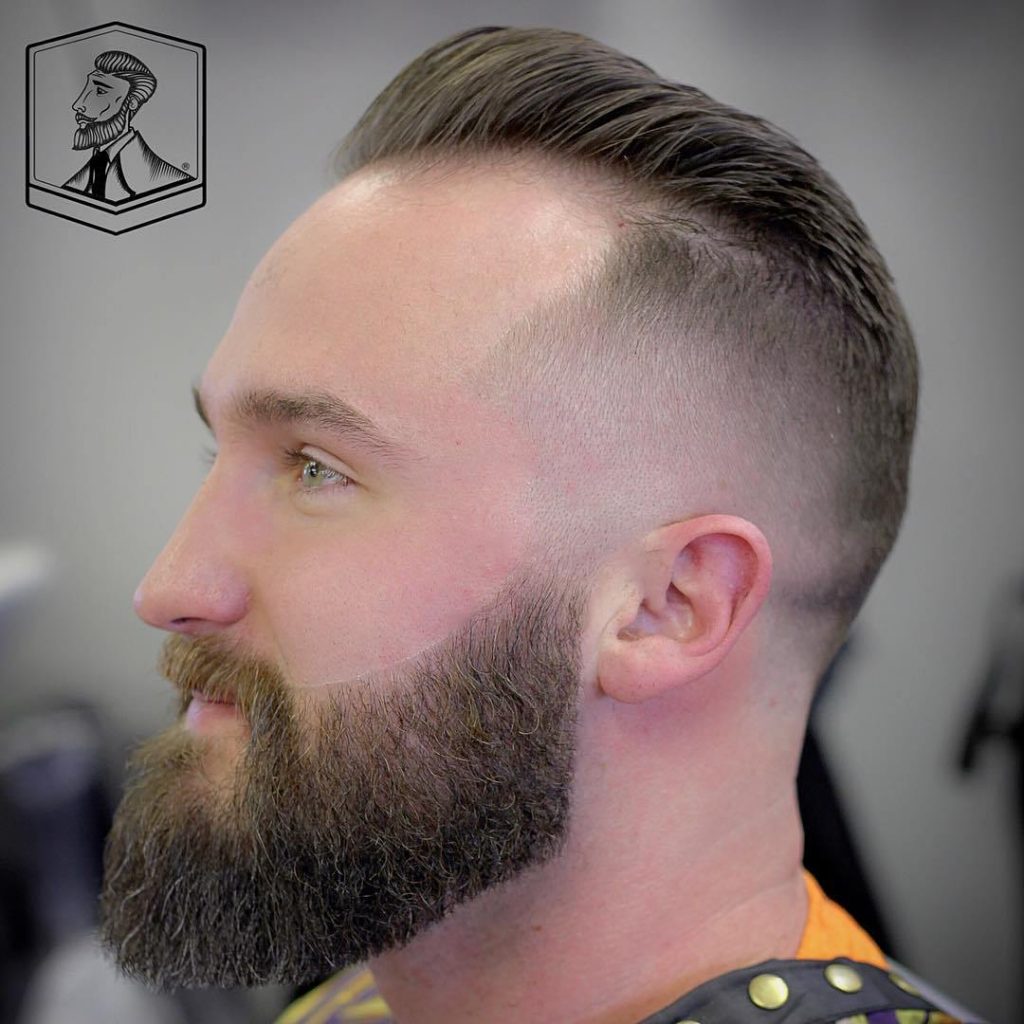
Many start to notice the early stages of male pattern baldness by their 30s, but they may begin as early as your late teenage years or early 20s. However, preventing further hair loss at the first sign of thinning is possible. Finasteride and Rogaine are two known treatments that might prevent further hair loss seen with androgenetic alopecia.
Patchy hair loss (alopecia areata)
Other signs of male-pattern baldness include thinning hair and a hairline that moves farther back on your head (receding hairline). Genetics plays a significant role in hair thinning, particularly in conditions like androgenetic alopecia (pattern baldness). This type of hair loss is often hereditary and can affect both men and women. Female pattern baldness is a type of hair loss that affects women and people assigned female at birth (AFAB). It causes you to lose hair on the skin covering your head (scalp). Female pattern baldness is a very common type of hair loss that affects women and people assigned female at birth.
What is the prognosis for hair loss in women?
However, it can affect you psychosocially (how society and social groups affect your thoughts and emotions) and psychologically (how you think about yourself and your behavior). Another method is to wear a hat or a hairpiece such as a wig or toupee. The wig is a layer of artificial or natural hair made to resemble a typical hair style. In the United States, the best wigs – those that look like real hair – cost up to tens of thousands of dollars.
Hair loss
In the middle and later stages of female pattern baldness, you’ll lose hair on either side of your part and toward the front of your scalp. You can change how you care for your hair, which can prevent hair loss. Once you damage a hair follicle, hair cannot grow from that follicle. Having many damaged hair follicles creates permanent bald spots.

It’s best to see a healthcare professional for any unexplained hair loss so they can determine the underlying cause and best course of treatment. This usually happens because of radiation treatment or chemotherapy. This usually isn't noticeable because new hair is growing in at the same time. Hair loss occurs when new hair doesn't replace the hair that has fallen out. In the type of patchy hair loss known as alopecia areata, hair loss occurs suddenly and usually starts with one or more circular bald patches that may overlap.
For example, anagen and telogen shedding may stop with time. Managing any underlying health conditions improves hair loss. And early treatment of alopecia may reduce the speed of thinning and promote regrowth. A healthcare provider can tell you more about what to expect in your situation.
Anti-aging guru Bryan Johnson, 46, claims he beat balding and stopped going gray: 'It's been a lot of hard work' - New York Post
Anti-aging guru Bryan Johnson, 46, claims he beat balding and stopped going gray: 'It's been a lot of hard work'.
Posted: Mon, 19 Feb 2024 08:00:00 GMT [source]
Laser therapy
For most people, the lost hair grows back, and you maintain a full head of hair. But illness, hormonal changes, stress, aging and inherited conditions can interfere with your hair’s growth cycle. More hair falls out, but new strands don’t always grow back. Baldness is usually most noticeable on the scalp, but can happen anywhere on the body where hair grows.
Female pattern baldness is a common condition that affects many women and people assigned female at birth after menopause. Many people with female pattern baldness accept it as part of the aging process and don’t see a healthcare provider. Reach out to your healthcare provider as soon as you notice signs of female pattern baldness, especially if it causes stress, anxiety or depression. Medications and treatments are available that can stop or reverse female pattern baldness. Male pattern baldness (androgenic alopecia) is a type of hair loss that affects people assigned male at birth (AMAB). It causes you to lose hair on the skin covering your head (scalp), and your hair doesn’t grow back.
A doctor may recommend dietary changes and supplements to treat a nutritional deficiency. Treatment for this condition depends on the cause but may include a topical solution of minoxidil (Rogaine). You should only take biotin, iron, or zinc when your blood test shows that you have a deficiency. If your levels are normal, taking a supplement can be harmful.
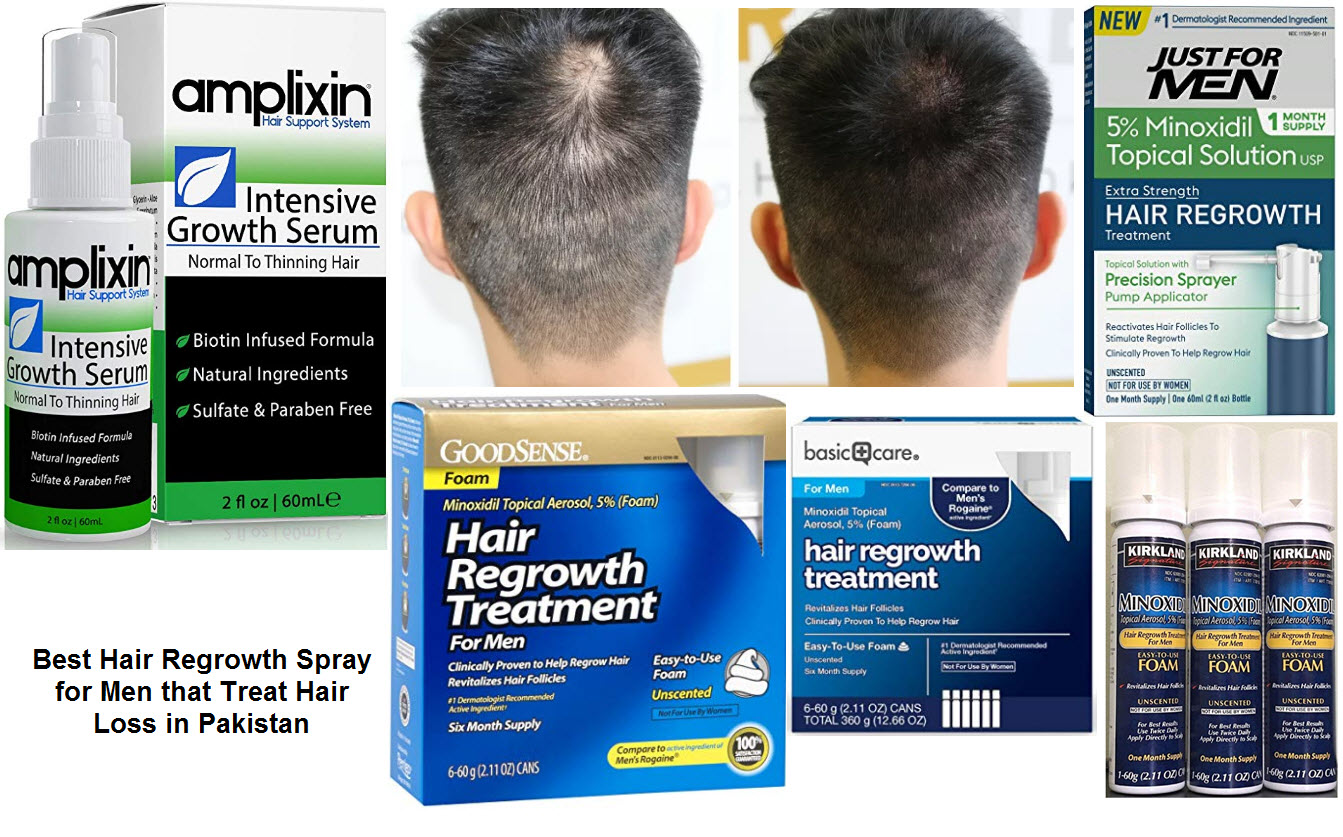
For example, if you take too much iron, you can develop iron poisoning. Early signs of this include stomach pain and vomiting. If your blood test reveals that you’re not getting enough biotin, iron, or zinc, your dermatologist may recommend taking a supplement. If you’re not getting enough protein, your dermatologist can tell you how to boost your intake. More studies are needed to find out who is most likely to benefit from this treatment and whether these devices cause long-term side effects. To use minoxidil, you apply it to the scalp as directed, usually once or twice a day.

Hair loss of this type generally follows a pattern, such as M-shaped hairline recession or thinning at the top of your head. Instead, they predominantly experience thinning throughout the top of the scalp, which manifests as a widening hair part. The term “balding” is most commonly used to refer to androgenetic alopecia, or male or female pattern hair loss. Although you can’t prevent male pattern baldness, there are ways to slow down hair loss. Some options include medications such as Finasteride (Propecia, Proscar) and minoxidil (Rogaine, Ioniten), laser therapy, and hair transplant surgery. Finasteride (sold as Propecia and Proscar) is a prescription medication used mainly to treat male pattern baldness by reducing the hormone DHT, which can shrink hair follicles.